Need Professional Help With Your Letters?
Get a quote for our specialized EB1A & EB2-NIW letter writing services
*We are professional writers specializing in crafting compelling recommendation letters and cover letters. For legal advice, please consult an immigration attorney.
The green card, formally known as a “permanent resident card,” is an essential document for individuals seeking permanent residency within the United States. The history of the green card dates back to the early 20th century, and its design and features have evolved significantly over the years. Understanding the purpose and origin of green cards provides insights into the significance of this document in the context of immigration to the United States.
What is a Green Card and its History?
First introduced as the Alien Registration Receipt Card (Form I-151) by the Immigration and Naturalization Service (INS), the green card serves as evidence of an individual’s permanent resident status in the U.S. The distinct green color of the card led to its colloquial name, “green card,” and it has become synonymous with lawful permanent residency. The historical evolution of the green card reflects the changing landscape of immigration laws and policies, emphasizing the importance of this document in the U.S. immigration system.
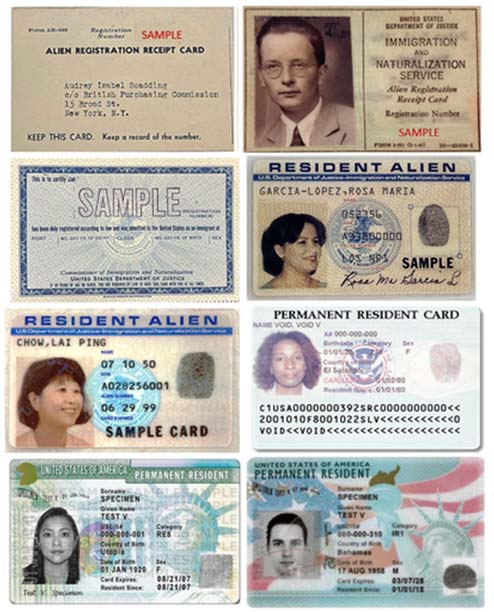

The Green Card has undergone several transformations over the years, and its color has not always been green. If you look at the image above, from the top left, we see the progression: the original Alien Registration Receipt Form Card (1940); Form I-151 (1946), the initial Green Card; Form I-151 (1964); Form I-551 (1977), the updated machine-readable Green Card; Form I-551 (1989), marking the introduction of an expiration date; Form I-551 (1997); Form I-551 (2010), which reintroduced the green coloration; and finally, Form I-551 (2017) before the 2023 version was unveiled.
Understanding the Purpose and Origin of Green Cards
The primary purpose of the green card is to provide evidence of an individual’s lawful permanent resident status in the U.S. It serves as a crucial identification document for individuals without U.S. citizenship, enabling them to live and work within the country. The origin of green cards can be traced back to the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952, which established the legal framework for granting permanent residency to foreign nationals.
Historical Evolution of the Green Card
The historical evolution of the green card reflects the changes in immigration laws and policies over the decades. From its early iterations as Form I-151 to the current version of the card, the design, security features, and information displayed on the card have undergone significant transformations to align with the evolving needs of the U.S. immigration system. The process of obtaining a green card has also evolved to incorporate modern application procedures and security measures.
Notable Changes in Green Card Design Over Time
The design of the green card has undergone notable changes in terms of its physical appearance, security features, and the inclusion of relevant information. These changes have been aimed at enhancing the security and integrity of the document, as well as ensuring that it meets the evolving standards of identification and verification in the U.S.
Types of Green Cards and Application Process
For individuals seeking permanent residency in the U.S., understanding the different types of green cards available and the application process is critical. The diverse categories of green cards cater to various immigration pathways, including family-based sponsorships, employment-based preferences, and special immigrant categories. The application process for obtaining a green card involves a series of steps and requirements that applicants must fulfill to secure their permanent resident status.
Different Types of Green Cards Available
The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) offers different types of green cards, each tailored to specific immigrant categories and eligibility criteria. These include family-based green cards, employment-based green cards, diversity visa lottery green cards, and special immigrant green cards, among others. Understanding the distinctions between these categories is crucial for individuals seeking to obtain a green card through the most suitable pathway.
Application Process for Obtaining a Green Card
The process of applying for a green card involves submitting the appropriate forms, supporting documentation, and undergoing necessary biometric and background checks. Applicants may also be required to attend interviews and provide evidence of their eligibility for permanent residency. Understanding the application process and adhering to the requirements outlined by USCIS is essential for a successful green card application. We suggest that you consult the attorney’s first to see if you qualify. And then, if it’s EB1 and EB2 NIW, you could also self-petition and save costs. Unsure of how to go about it? You could hire us to help you write the green card application. While we are not lawyers, we are skilled writers and journalists who have helped people secure green cards with our persuasive writing.
Renewal and Update Procedures for Green Card Holders
Green card holders are responsible for ensuring that their cards remain valid and up to date. Understanding the procedures for renewing and updating green cards is crucial for maintaining lawful permanent resident status within the U.S. Green card renewals involve submitting the Form I-90 to USCIS and providing evidence of continued eligibility and residence in the country.
Security Features and New Redesign
The security features embedded in modern green cards play a vital role in safeguarding against identity theft, fraud, and counterfeiting. The recent redesign of the green card aims to enhance its security measures and authentication features, ensuring the integrity of the document and minimizing the risk of misuse. The January 2023 version of the green card incorporated advanced security features and design enhancements.
Security Measures Embedded in Modern Green Cards
Modern green cards incorporate advanced security measures, including holographic images, embedded microchips, and intricate designs that are difficult to counterfeit. These features are intended to prevent unauthorized alterations or replication of the document, enhancing its authenticity and reliability as a form of identification for permanent residents in the U.S.
Implications and Benefits of the Green Card Redesign
The redesign of the green card carries significant implications for both green card holders and immigration authorities. The enhanced security features and updated design elements provide greater assurance of the card’s authenticity and reinforce its role as a trusted proof of lawful permanent residency. Furthermore, the redesigned green card is expected to streamline verification processes and support efficient immigration management.
Changes in the 2023 Version of the Green Card
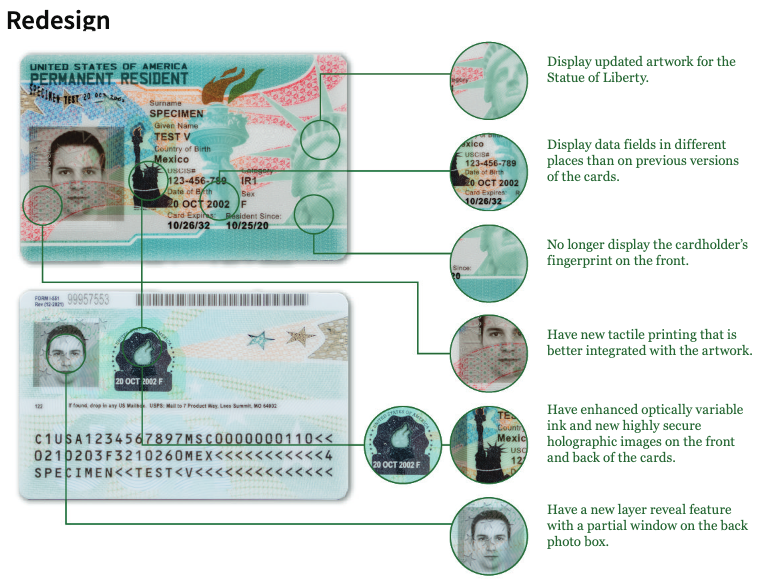
With the 2023 version of the green card, there are advanced biometric technologies, tamper-resistant materials, and additional security elements that further elevate the document’s integrity and resilience against fraud and misuse. The new version aims to set higher standards for secure identification and establish the green card as a reliable credential for lawful permanent residents. The changes include better artwork details, smoother integration of tactile printing, improved ink with optical effects, more secure holographic images on both sides of the cards, a feature revealing a layer with a window on the back photo box, and data fields placed differently compared to older versions.

Lost or Expired Green Cards: What to Do?
Dealing with lost or expired green cards requires prompt action to safeguard one’s lawful permanent resident status and ensure uninterrupted documentation of immigration status. Understanding the procedures for handling lost green cards and addressing expired card issues is essential for green card holders seeking to maintain their lawful presence within the U.S.
Procedures for Handling Lost Green Cards
In the event of a lost or stolen green card, individuals must report the incident to USCIS and apply for a replacement card. This involves submitting the Form I-90 and providing details of the circumstances leading to the card’s loss or theft. Understanding the steps for reporting and replacing lost green cards helps individuals navigate the process effectively.
Dealing with Expired Green Cards
Green card holders must be mindful of the expiration date on their cards and take proactive steps to renew them before they expire. Operating with an expired green card can lead to significant legal and immigration consequences, potentially jeopardizing one’s permanent resident status. Understanding the implications of expired green cards and promptly initiating the renewal process is crucial for maintaining lawful residency in the U.S.
Steps for Replacing or Updating Green Cards
For individuals in need of replacing or updating their green cards, understanding the specific steps outlined by USCIS is imperative. This involves completing the appropriate forms, gathering supporting documents, and following the necessary procedures to ensure the timely issuance of a new, valid green card. Compliance with the replacement and update processes is essential for preserving one’s lawful permanent resident status.
Living and Working with a Green Card: Rights and Responsibilities
Green card holders enjoy certain rights and privileges while also shouldering specific responsibilities and obligations within the U.S. Understanding the implications of holding a green card, both in terms of rights and responsibilities, is essential for individuals navigating the intricacies of permanent residency and immigration status.
Rights and Privileges of Green Card Holders in the USA
Green card holders have the right to live and work in the U.S. indefinitely, pursue educational opportunities, and access social benefits offered to permanent residents. They also have the option to sponsor qualifying relatives for immigration to the U.S., making family reunification a significant benefit of permanent residency. Understanding and exercising these rights responsibly is crucial for green card holders.
Responsibilities and Obligations of Green Card Holders
Green card holders are required to fulfill certain responsibilities, including maintaining a permanent residence in the U.S., abiding by federal, state, and local laws, and registering with the Selective Service System if applicable. Additionally, green card holders are expected to file income tax returns and adhere to the immigration laws governing their permanent residency status. Understanding and fulfilling these obligations is essential for maintaining lawful permanent residency.
Impact of Green Card Status on Immigration and Employment
The possession of a green card significantly impacts an individual’s immigration and employment prospects within the U.S. It provides a pathway to citizenship, offers eligibility for various employment opportunities, and facilitates international travel. Understanding the implications of green card status on immigration and employment enables individuals to leverage their permanent residency to pursue their aspirations and contribute to the U.S. society and economy.
FAQ
What is the history of the green card?
The green card, also known as a permanent resident card, has a history dating back to the Alien Registration Act of 1940. It has gone through various redesigns and updates over the years.
How can I renew my green card?
To renew your green card, you can file Form I-90, Application to Replace Permanent Resident Card, with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
What is an alien registration receipt card?
An alien registration receipt card is another name for the green card, which is evidence of your permanent resident status in the United States.
How can I apply for a green card?
You can apply for a green card through various paths, such as family-based green card sponsorship, employment-based green card sponsorship, the green card lottery, or as a special immigrant.
What does a green card renewal involve?
The green card renewal process typically requires filling out the Form I-90, submitting supporting documents, paying the required fees, and attending biometrics appointments if necessary.
What is a conditional permanent resident?
A conditional permanent resident holds a green card that is valid for a limited period, usually granted through marriage-based immigration or entrepreneur programs.
What are the previous versions of the green card like?
Previous versions of the green card included designs such as the I-151 card and have undergone changes in appearance and security features over time.
What should I do if my green card is lost?
If your green card is lost or stolen, you should immediately apply for a replacement card by filing Form I-90 with the USCIS.
What are the steps to read a green card?
To read a green card, you can find important information on both the front and back of the card, including your name, alien number, and the card’s expiration date.
What are the eligibility requirements to get a green card?
The eligibility requirements to get a green card vary depending on the immigration category you are applying under, such as family-based, employment-based, refugee or asylee status, and more.

